Fertilizer Byproduct Creates Alternative Fuel
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Technology
Waste liquids can create fuel through submerged plasma arc gasification
What began as a way to transform manure into fertilizer has created a byproduct that can be utilized as an alternative fuel.
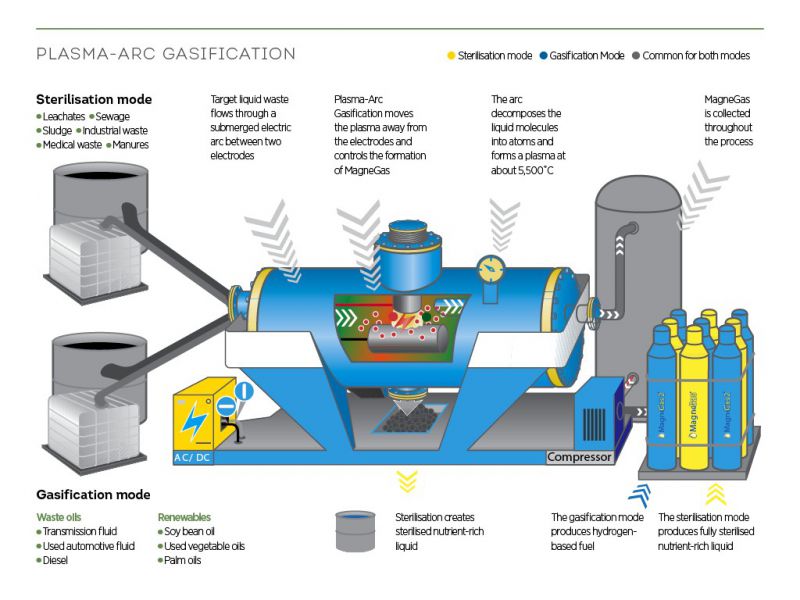 MagneGas Corp., a technology company, discovered that through submerged plasma arc gasification various waste liquids can create fuel through two methods. In gasification mode, inputs can include transmission fluid, automotive fluid, diesel, soybean oil, vegetable oil, and palm oil. In sterilization mode, inputs can include leachates, sewage, sludge, industrial waste, medical waste and manure.
MagneGas Corp., a technology company, discovered that through submerged plasma arc gasification various waste liquids can create fuel through two methods. In gasification mode, inputs can include transmission fluid, automotive fluid, diesel, soybean oil, vegetable oil, and palm oil. In sterilization mode, inputs can include leachates, sewage, sludge, industrial waste, medical waste and manure.
Luisa Ingargiola, chief financial officer for MagneGas, discusses the MagneGas alternative fuel and the company’s hopes to burn it with less efficient fuels and wastes resulting in improved emissions in the future:
The process or technology behind creating the fuel
The submerged plasma arc gasification is a patented technology that was originally conceived to safely transform manure into a usable fertilizer. Later, it was discovered that the gas byproduct produced can be used as a cleaner, safer and more efficient fuel than other industrial gas products currently available in the market.
Plasma-arc gasification technology can be used in either the gasification mode or the sterilization mode, each having its own benefits for the industrial gas market. In gasification mode, the technology takes renewable liquid wastes, such as readily available liquid feedstocks, soybean and other vegetable oils, converting them into a hydrogen-based gas alternative.
The benefits of MagneGas?
A few of the benefits of MagneGas2 include better solutions for waste management, water scarcity, renewable energy and industrial safety. Our technology converts waste into reusable energy and products for multiple functions.
In sterilization mode, it replaces the need to use limited freshwater resources through sterilizing waste water for agriculture and municipal services, potentially improving the health and environment of communities.In gasification mode, MagneGas2 is the only renewable cutting fuel on the market that is made from waste and renewable fuels. For industrial gas workers, MagneGas2 reduces the risk of air toxicity, with less volatility than other gases, providing safer working environments.
The MagneGas fuel is currently being used by several major utility companies and manufacturing companies. The fuel is being used at a NASA facility for demolition and has been approved for use by the New York Fire Department. In addition, the company has sold its first Gasification system to a gas distribution company in Louisiana, and expects that system to be installed and operational this year.
What industries utilize it?
We are able to service many industries and provide green solutions to previous waste and health concerns. We address sterilization issues in the industries of water management, medical waste, sewage, industrial waste and agriculture. In gasification mode, we access industries including the industrial gas market, welding, repairs, and metal cutting.
The future of this technology?
We are working through verification for our latest utilization of MagneGas, Co-Combustion.
Co-Combustion is burning MagneGas2 with less efficient fuels and wastes resulting in improved emissions, improved efficiency and a dramatic reduction in CO2. Markets for Co-Combustion include coal, medical waste, incineration and heavy oils. We expect verification by the end of this year.
On a more global scale, we are looking into several different international markets which struggle with their waste management or looking for their own renewable source of energy.What began as a way to transform manure into fertilizer has created a byproduct that can be utilized as an alternative fuel.
Source: Waste 360
Media
Taxonomy
- Water Scarcity
- Renewable Energy
- Waste Management