Why is there an Increase of Interest in Geothermal Energy
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Technology
Power producers around the world are increasingly turning their attention to the heat beneath our feet.
At 2:46 p.m. local time on Friday, March 11, 2011, Japan was rocked by the largest earthquake ever to strike its shores. The 9.1 magnitude quake triggered a devastating tsunami that killed more than 15,000 people. It also took out the back-up emergency generators that cooled the reactors at the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant complex, causing a series of catastrophic meltdowns.
But amid the chaos, the Yanaizu-Nishiyama geothermal power plant in Fukushima prefecture didn’t miss a beat. Along with two more of the nine geothermal power plants in the region, the 65-megawatt facility continued to generate power, even as many other power plants around them failed because of damaged equipment and transmission lines.

The Yanaizu-Nishiyama geothermal power plant, in Fukushima Prefecture, Japan, was able to continue generating electricity despite the devastation of the 2011 tsunami. Photo by Σ64 (Wikimedia Commons/Creative Commons)
“This is big news for many geothermal people around the world,” says Kasumi Yasukawa, principal research manager at the Institute for Geo-Resources and Environment in Japan’s National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology.
In a country as seismically active as Japan, it was a clear signal that geothermal energy was worth investing in.
Geothermal electricity generation might not have the high-tech flashiness of solar, or the romance of wind and wave, but it’s the solid, steady workhorse of the renewable energy race. The never-flagging heat lurking at various depths below the Earth’s surface is tapped to produce steam that is used to drive turbines and generate electricity. This heat can also be used more directly to warm spaces or swimming pools, but sustainable electricity generation is the goal that most have in their sights.
“If you want to know what you could run an industrial society off of, it would be hydro and as much geothermal as you could find,” says Susan Krumdieck, who heads the Advanced Energy and Material Systems Lab at the University of Canterbury in New Zealand.
Star on the Rise
Wind and solar energy have many excellent qualities, but reliability isn’t necessarily one of them. When the wind drops off, or the sun sets, something else has to step in. And increasingly, nations are turning to geothermal to deliver that stability.
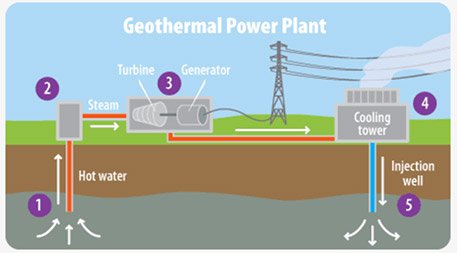
Geothermal power plants draw hot water up from the ground and use the energy it contains to spin electricity-generating turbines. Graphic by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency
The use of geothermal electricity varies enormously around the world. In 2015, 24 countries had a total of around 13.3 gigawatts of geothermal power capacity. The United States is the single biggest, with just over 3,500 megawatts of capacity — although this only contributes around 0.3 percent of the nation’s electricity capacity — followed by the Philippines, Indonesia and Mexico in the 1,000 to 2,000 MW range.
Geothermal energy’s star seems to be on the rise. The Japanese government has committed to tripling its geothermal electricity capacity, from around 540 MW in 2011 to 1,500 MW, by 2030. El Salvador is aiming to source 40 percent of its electricity from geothermal by 2019 — up from around 25 percent — and in Kenya, geothermal energy has now taken over hydro as the top supplier of electricity, providing 51 percent of the nation’s electricity
Global geothermal generation capacity is expected to grow from 13.3 gigawatts in 2015 to 32 GW in the 2030s. Graphic by Aleszu Bajak.
But these countries, and others such as Iceland and New Zealand, have one big advantage: Their volcanic geology and seismic activity means the heat is relatively close to the surface and often in close contact with water, and therefore much easier to tap. But not all countries are so lucky, and this is where enhanced geothermal electricity comes into play.
Enhanced Geothermal
Geothermal electricity generation needs three things to be viable: heat, fluid and a substrate permeable enough to allow movement of fluid through it and up to the surface, where the steam is used to turn power-producing turbines. In the case of conventional geothermal energy — sometimes called hydrothermal energy — all three of these elements naturally occur together.
However this is the exception rather the rule. For the majority of countries, the heat is there, but the fluid, and in some cases the permeability, are not.
Enhanced geothermal involves drilling wells into the hot rock, and forcing fluid — water or brine — into the hot rock through fractures or permeable areas. The heated water is then extracted via another well and put to work generating electricity.
“The hydrothermal systems that have been developed to date are by and large low-hanging fruit,” says Robert Podgorney, director of the Snake River Plain Geothermal Consortium and Idaho National Lab FORGE — Frontier Observatory for Research in Geothermal Energy — Initiative. “But the elephant in the room is the enhanced geothermal; the source base dwarfs all of production to date.”
For example, a 2008 report by the U.S. Geological Survey estimated there are more than 500,000 MW of untapped enhanced geothermal energy in the western United States alone, an order of magnitude greater than available conventional geothermal resources. FORGE is the U.S. government’s up to US$31 million push to shift enhanced geothermal electricity generation up a gear.
Read full article at: Ensia
Media
Taxonomy
- Energy
- Geothermal
- Energy Efficiency
- Water & Geotechnical Engineering
- Energy-Water Nexus
- Plant Engineering
- Energy Efficiency
