How to Safeguard Your Monitoring Wells from Environmental Contaminants?
Published on by Phil Lundman in Social
Monitoring wells help track groundwater quality, but they can only provide accurate data if they are kept clean and safe. Chemicals, petroleum spills, and surface runoff can all enter the well, causing incorrect readings and perhaps damaging the ecosystem. Protecting your monitoring equipment is critical to getting reliable data and keeping with environmental standards.
To keep monitoring wells safe, use proper sealing techniques, install high-quality well plugs, and conduct frequent inspections. These basic actions help avoid contamination and keep the well operational for long-term monitoring.
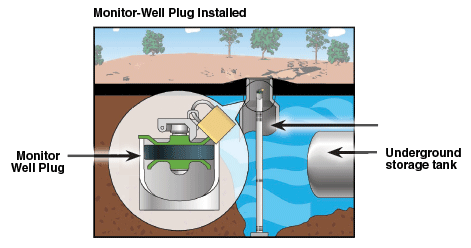
Understanding the Risks of Well Contamination
Potential Sources of Contamination
Contaminants can enter a monitoring well through a variety of means, including:
- Surface runoff - Rainwater can carry dirt, bacteria, and contaminants from highways, farms, and industrial locations into wells.
- Chemical spills - Leaks from nearby storage tanks, insecticides, or industrial chemicals can contaminate groundwater.
- Petroleum leaks - Fuel spills or underground storage tank failures can inject hydrocarbons into the water, altering its quality.
- Improper sealing - Contaminants might enter the well through gaps or cracks in the casing.
Consequences of Compromised Monitoring Wells
- Inaccurate data - Contaminated wells produce inconsistent test findings, making assessing groundwater quality challenging.
- Regulatory infractions - Government agencies, such as the EPA, require proper well protection. Failure to comply can result in sanctions.
- Environmental impact - A contaminated well might spread pollution instead of detecting it, worsening the situation.
Understanding these risks allows well owners and operators to take necessary precautions to avoid contamination and maintain well integrity.
Proper Well Construction and Sealing
The importance of selecting high-quality well materials
Using long-lasting, high-quality materials is critical for maintaining monitoring wells safe and free of pollution. Inferior materials can deteriorate over time, allowing pollutants into the well and contaminating water samples. Strong, chemically resistant materials contribute to well integrity, ensuring consistent data collection and long-term performance.
Using EPA-Compliant Locking Well Plugs for Effective Sealing
Locking well plugs create a tight seal, preventing impurities from entering the well. To comply with EPA requirements, these plugs must be constructed for a secure fit and made of long-lasting, non-corrosive materials. A proper locking mechanism also prevents tampering, keeping the well undisturbed and the data correct.
Benefits of Chemical and Petroleum Resistant Seals
To avoid infiltration in difficult areas, well plugs must have chemical and petroleum-resistant sealing. These specialized seals
- Prevent chemical seepage from fertilizers, industrial waste, and fuel spills.
- Resist degradation due to oil, chemicals, and harsh weather.
- Ensure a long-lasting seal, minimizing the need for frequent changes.
Choosing a well stopper with nitrile O-rings and corrosion-resistant components provides an additional layer of protection, helping in the maintenance of water quality and the prevention of contamination.
Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Routine inspection and maintenance are critical for maintaining monitoring wells safe and contamination-free. Well plugs and seals degrade with time, resulting in leaks and incorrect groundwater readings. Regular inspections assist in detecting problems early and ensuring compliance with environmental requirements.
How Often to Check Well Integrity?
Quarterly inspections – Check the well plugs every three months to guarantee a tight seal and proper operation.
- After severe weather - Heavy rain, flooding, or extreme temperatures can damage well components, requiring a prompt inspection.
- Before sampling - Always check the plug's condition before taking groundwater samples to avoid contamination.
Conclusion
Protecting monitoring wells is critical for reliable data collection and environmental safety. Key procedures include recognizing contamination risks, using high-quality well plugs, ensuring a secure fit, locking the well, and performing frequent inspections.
Durable well locking plugs help to prevent leaks, withstand chemicals, and maintain well integrity. Investing in appropriate sealing and regular maintenance improves long-term well protection, reduces contamination concerns, and promotes compliance. Stay proactive and secure your wells with the proper plugs and best practices.
Taxonomy
- Plumbing
- Plumbing
- Pipe Plugs