Microplastics in WWTPs: Sources, properties, removal efficiency, removal mechanisms
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Technology
Microplastics in wastewater treatment plants: Sources, properties, removal efficiency, removal mechanisms, and interactions with pollutants
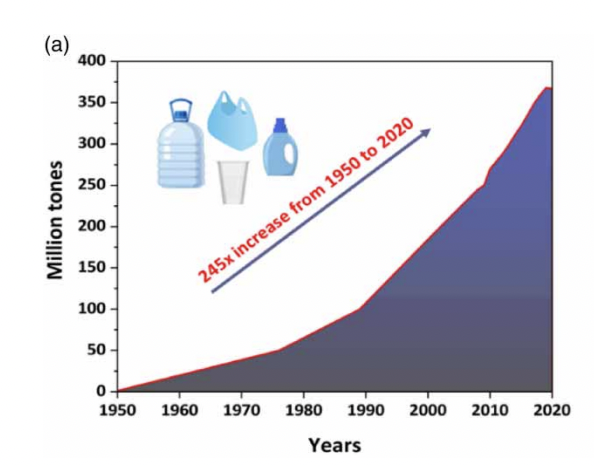
ABSTRACT Since wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) cannot completely remove microplastics (MPs) from wastewater, WWTPs are responsible for the release of millions of MPs into the environment even in 1 day. Therefore, knowing the sources, properties, removal efficiencies and removal mechanisms of MPs in WWTPs is of great importance for the management of MPs. In this paper, firstly the sources of MPs in WWTPs and the quantities and properties (polymer type, shape, size, and color) of MPs in influents, effluents, and sludges of WWTPs are presented. Following this, the MP removal efficiency of different treatment units (primary settling, flotation, biological treatment, secondary settling, filtrationbased treatment technologies, and coagulation) in WWTPs is discussed. In the next section, details about MP removal mechanisms in critical treatment units (settling and flotation tanks, bioreactors, sand filters, membrane filters, and coagulation units) in WWTPs are given. In the last section, the mechanisms and factors that are effective in adsorbing organic–inorganic pollutants in wastewater to MPs are presented. Finally, the current situation and research gap in these areas are identified and suggestions are provided for topics that need further research in the future.
See full paper attached
Media
Taxonomy
- Micropollutants
- Polymers & Plastics