The features of operation of an ion exchanger in the process of water desalination | tiwater.info
Published on by Ivan Tikhonov in Technology
This article discusses the influence of carbon dioxide contained in water on the process of ion exchange desalination of water with a mixed bed ion exchange resin. Experimental data are presented. Recommendations are given for conducting the desalination process using a mixed bed ion exchange resin.
The main indicator of the quality of ultrapure water is the specific electrical conductivity of water (electrical conductivity). The minimum possible electrical conductivity of water is 0.055 µS/cm. It is believed that at this value of electrical conductivity, water does not contain substances that can transfer an electric charge. The electric charge in water is transferred by means of ions. There are several ways to remove ions from water. Currently, the most common are 2 ways:
1-ion exchange
2- reverse osmosis
To remove ions by ion exchange, cationic and anionic resins in the form of H+ and OH – are used, respectively. That is, all cations contained in water are replaced on the cationite by hydrogen cations (H+) and anions are replaced on the anionite by hydroxyl anions (OH-). As a result, water molecules are obtained and, accordingly, all ions are removed from the water, provided that the concentration of cations is equal to the concentration of anions in mg-EQ/l.
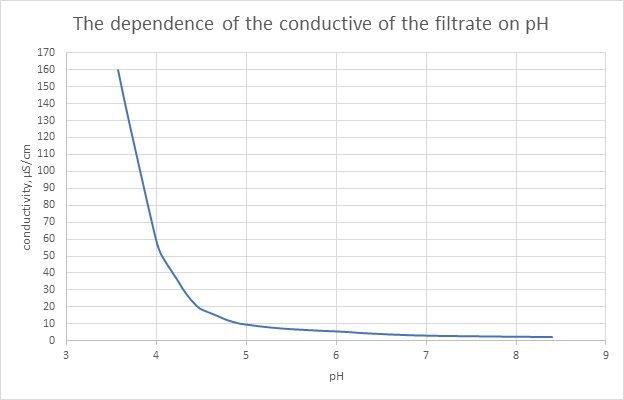
You can see the full version in my site https://tiwater.info/en/
Attached link
https://tiwater.info/en/the-features-of-operation-of-a-mixed-bed-ion-exchanger-in-the-process-of-water-desalination/Taxonomy
- Desalination
- Reverse Osmosis
- Ion Exchange Resin