Coliform Bacteria in Water Wells
Published on by Marina A, Previously Key Account and Content Manager at AquaSPE AG in Academic
Coliform bacteria are a commonly used as a test for the quality of food and water. Their presence indicates the possible presence of pathogens.
Coliform bacteria can be found in the aquatic environment, in soil (but the bacteria washed into the ground is usually filtered out as the water goes to the groundwater aquifers) and feces of warm-blooded animals .
Most coliform bacteria do not cause illness, but the presence of some types of coliform bacteria indicates the presence of feces.
In most cases, the concentration of pathogens from fecal contamination is small and the variety of pathogens is large. Testing for them is, therefore, impractical. Water is, instead, tested for coliform bacteria as an indicator and indirect sign that other pathogens may be present.
Reasons for coliform bacteria being used for testing water quality:
Coliforms are found in large amounts
Easy to identify
Respond to the environment and water treatment in similarly as pathogens.
The only certain way to know if bacteria is present in water is to do a test. Bacteria cannot be detected by looks, smell nor taste.
The most basic test is to test for coliform bacteria to get the overview of the sanitary condition of water.
Total coliforms are found in soil, in water not influenced by surface water, in human or animal waste.
Fecal coliforms are present significantly in the gut and feces of warm-blooded animals. Fecal coliforms are a more accurate indication of animal or human waste.
Escherichia coli ( E. coli ) is a species in the fecal coliform group. It is the most reliable indicator of the presence of pathogens because it does not grow and reproduce in the environment.
Coliform contamination is most probable to happen during wet weather so it is safest to test you water well in late spring or early summer. Coliform bacteria prefer warmer temperatures. Highest number of bacteria can be found a few weeks after rainy weather.
A recent Penn State study tested 38 wells at different times during the year – temperature and precipitation. During cold and dry weather more than 50% of the wells which were previously contaminated, did not contain bacteria anymore.
The most common test is for total coliform bacteria. If the test is positive for coliform bacteria, you are at risk of contracting a water-borne disease and other tests for fecal bacteria and E.coli may be necessary. 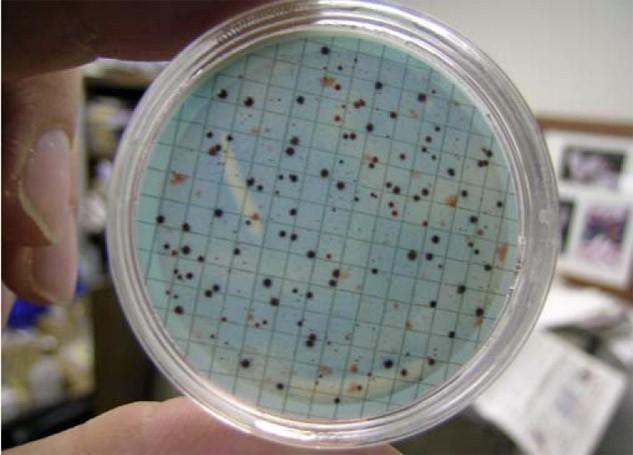
Image: A petri dish showing coliform bacteria that have grown after 24 hours of incubation from filtration of 100 mL of well water.
Image source: extension.psu.edu/natural-resources/water/drinking-water/water-testing/pollutants/coliform-bacteria
What if your well water tested positive for coliform bacteria?
Do not drink the water.
Boiling water before use is an efficient short-term and immediate solution for dealing with coliform bacteria contamination. The water should be boiled for at least a minute before drinking.
Confirm the results: make sure the test result is accurate.
Perform an E.coli test to establish how severe the problem is.System maintenance: the maintenance may solve the coliform bacteria problem.
Some of the causes for coliform bacteria in water wells which may need to be adressed:Lack of or a defective water cap
Well flooding
Contaminant seeping along the outside of the well casing
Contaminant seepage through the well casing
Shock chlorination: shock chlorination can help in cases of temporary or one-time coliform bacteria contamination (heavy rain or installation of a submersible pump).
Continuous disinfection: if shock chlorination does not help, installing a system that will continuously treat the water may be necessary.
Chlorination - a feed system that injects:
a chlorine solution (sodium hypochlorite)
dry powder (calcium hypochlorite).
The Chlorine is consumed as it kills bacteria.
Chlorine demand is the amount of chlorine needed to kill the bacteria and oxidize the impurities in water.
The pH and temperature will affect the chlorine demand.
Contact time should be around 30 min or shorter with larger chlorine doses, however, chlorine taste and smell will then be present.
Long-term solutions for coliform bacterial water well contamination:
Connecting to the public water system
Inspecting and repairing the well defects
Constructing a new well
Continuous disinfection equipment
Bottled water use for drinking and food preparation.
Sources:
Media
Taxonomy
- Bacteria
- E. coli
- Sanitation
- Water & Sanitation
- Sanitation & Hygiene
- Sanitation Services
- E. coli
1 Comment
-
Hello
All sanitation systems discharge wastewater into the environment in one form or another. There are many management infrastructures but there is no practice of purification other than passing excreta from one point to another, the other being the environment.
Of the 7 billion of the terrestrial population more than a billion and a half practice defecation in the open air.
To this quota must be added 3 billion of the population of which all the facilities of storing excrements disperse their excrements in the environment
The latest addition to the 2 billion of the population in sewage treatment plant infrastructure which opens the bypass of clearance at the entrance of the STEP to avoid the usbmersions during the heavy rainfall precipitation
The last one being the 2 billion of the population who pour into the environment its excrements during the floods
It is therefore quite normal to find traces of fecal matter in the groundwater reserves