pH Adjustments
Published on by Marina A, Previously Key Account and Content Manager at AquaSPE AG in Academic
pH is a numeric scale that indicates the acidity of an aqueous solution.
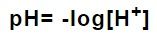 It is the negative logarithm to base 10 of the molar concentration of hydrogen ions, measured in units of mol/l. It is a measurement of the potential activity of hydrogen ions (H+) of the solution.
It is the negative logarithm to base 10 of the molar concentration of hydrogen ions, measured in units of mol/l. It is a measurement of the potential activity of hydrogen ions (H+) of the solution.
The pH scale has a range from 0 to 14, with the 7 indicating a neutral point.
- Solutions with a pH below 7 are acids.
- Solutions with a pH above 7 are bases.
- Distilled, pure water is neutral, neither acid nor a base, and has a pH of 7.
Since pH is measured in the logarithm scale, each whole pH value below 7 is 10 times more acidic than the next higher value.
Pure water is neutral, but when it is mixed with chemicals it can change its acidity. Additionally, mixing acids and bases can neutralize their effects.
Causes of pH variations in water:
- Soil composition through which the water moves, in its bed and as groundwater. Certain rocks can neutralize the acid while others have no effect.
Limestone can buffer – neutralize the acidification of freshwater. - Number of plants and organic matter in the water. Carbon dioxide is released when they decompose, and if forms the carbonic acid as it combines with water. It is a weak acid but in greater amounts in will lower the water pH.
- Chemicals in the water released by industries or individuals. Industrial effluents that are released in the environment, therefore, are required to have a certain pH value.
- Acid precipitation. Acid rain occurs when nitrogen oxides (NOx) and sulfur dioxide (SO2) in the air are combined with water vapor. They are products of car fumes and emissions from coal-fired power plants.
- Coal mine drainage. Sulfuric acid is formed when iron sulfide, which is found around coal mines, is combined with water.
pH standards for drinking water:
Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) maintains strict standards for appropriate pH levels in drinking water. Consuming excessively acidic or alkaline water is harmful, warns the EPA. Drinking water must have a pH value of 6.5-8.5 to fall within EPA standards , and they further note that even within the acceptable pH range, slightly high- or low-pH water can be unappealing for several reasons. High-pH water has a slippery feel, tastes a bit like baking soda, and may leave deposits on fixtures, according to the EPA website. Low-pH water, on the other hand, may have a bitter or metallic taste, and may contribute to fixture corrosion.
Aquatic life is greatly affected by the water pH. The natural range of most freshwater lakes, streams, and ponds is between 6 and 8.
Most organisms are adapted to a specific water pH and if it is even slightly changed they will die.
If the pH falls below 6, especially 5, it may cause damaging ecological effects.
- As the pH comes close to 5, planktons and mosses – non-desirable species start to invade and some fish populations disappear.
- If the pH is below 5, fish disappear and the bottom gets covered with undecayed matter, with moss is nearshore areas.
- Below 4.5 there is no fish.
Extreme pH values affect fish as they damage juvenile fish development and strip the slime coat of the fish flakes.
If the water pH is extremely alkaline, it may cause the fish to die, damage its gills, eyes and flakes.
The effect of pH on humans:
People have a higher tolerance for pH levels (drinkable levels range from 4-11 with minimal gastrointestinal irritation), there are still concerns.
pH higher than 11 and lower than 4 causes skin and eye irritation.
pH bellow 2.5 causes irreversible skin damage and organ linings.
Lower pH increases the risk of mobilized toxic metals absorption.
Above pH of 8 water cannot be disinfected effectively so other risks may occur.
* Outside the pH range of 6.5-9.5 pipes can corrode and be damaged and thus heavy metals toxicity is increased.
The pH is an important factor that determines water health.
pH adjustment systems:
There are two primary types of system design for pH adjustments – continuous and batch.
- Continuous flow
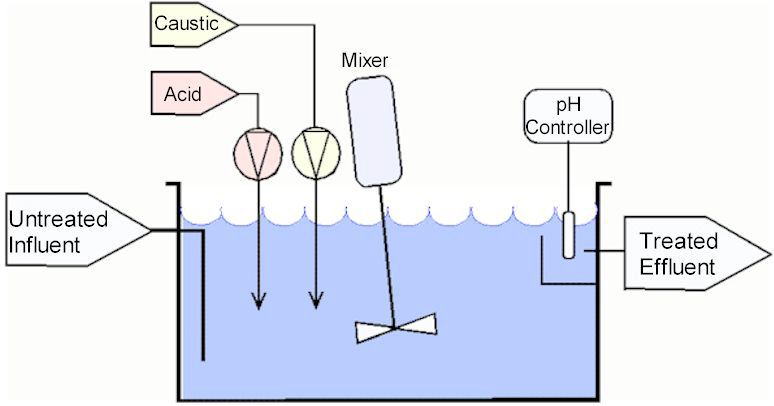
The tank is constantly full – the amount of influent entering it equal to the treated effluent exiting the tank.
The advantage of this system is that can handle relatively high flows. However, it is not certain that the effluent will always be in range.
- Batch
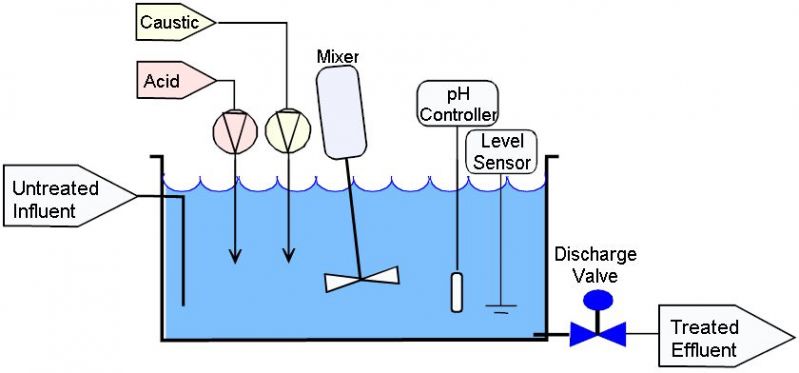
The batch has a fixed water volume, which is discharged only after fulfilling the criteria.
The influent enters the tank anywhere convenient and exits due to gravity near the bottom, where the port is located.
The batch volume is treated in one cycle.
** The systems shown here are simplified.
pH adjusting methods:
Raising the pH | Lowering the pH |
Neutralizing filters | Acid injections |
MgO beads | CO2 |
Soda ash/sodium hydroxide injections |
|
- Neutralizing filters
Neutralizing filters are used if drinking water is acidic.
The pH is increased by the addition of the neutralizing material.
It is important to highlight that the water hardness may increase.
(Water hardness is the amount of dissolved calcium and magnesium in the water - dissolved bicarbonate minerals - calcium bicarbonate and magnesium bicarbonate.)
Neutralizing filters are point-of-entry devices.
Water with pH greater than 6 is treated with calcium carbonate (limestone) and water with the pH below 6 is treated with the synthetic magnesium oxide.
Untreated water passes through a filter filled with either calcium carbonate or a synthetic magnesium oxide medium and the material dissolves in the water therefore raising the pH level.
The flow rate should not the greater than 2 l/s·m2. The bed should be deep enough to provide sufficient contact time.
The material in the neutralizing filter need refilling and regular backwaching.
If cartridge filters, that retain solids from passing through, are installed before the neutralizing filters, the neutralizing filters will last longer.
After the neutralizing filter a water softener can be added to regulate the water hardness.
The neutralizing filter may result in pressure loss, since the water passes through the finely ground neutralizing material.
The corrosion of the pressure tank and the well pump may occur since the neutralizing filters are installed after the pressure tank.
In case of a high flow rate, liquid injection systems are a better solution.
- Magnesium oxide beads in combination with reverse osmosis
Prill MgO beads are used when the water pH needs to be rasied.
They should be used after reverse osmosis.
Osmosis is a spontaneous movement of the molecules in the solvent through a semi-permeable membrane. The molecules tend to “go” to the in that direction that will equalize the concentrations of the two sides. Reverse osmosis is a process in which the particles move in the opposite direction than in natural osmosis. The contaminated fluid passes through the membrane and the suspended particles are separated from the liquid. For this process, pressure is needed – the hydrostatic pressure needs to be greater than the osmotic pressure.
Prilly Pure Water Beads raise and balance pH levels of the water to 8,7 without any chemicals.
The beads are made from magnesium oxide which is produced from naturally occurring salts of magnesium found in rich brine deposits located approximately 2,500 feet below ground. The resulting magnesium oxide is ‘prilled’ into small, hard pellets by a high temperature firing process which turns them into small ceramic-like pellets.
In addition to adjusting the pH, the beads lower the surface tension of water, remove toxins and pull out heavy metals from water.
Prilly Pure Water Beads last forever and never need to be replaced.
- Injection systems:
- Soda ash/sodium hydroxide injection
Soda ash/sodium hydroxide injections are used if the water is acidic.
When injected into a water system, soda ash (sodium carbonate) and sodium hydroxide raise the pH of water.
Injection systems are a point-of-entry system.
Soda ash or sodium hydroxide solution are injected in the water by a corrosion-resistant chemical feed pump.
The injections are installed before the pressure tank so that the tank ant plumbing systems are protected from corrosion.
Dual treatment is used if the water needs to be disinfected, in addition to being neutralized. A chlorine solution is added with the neutralizing chemical.
With the injection systems water with low pH can be effectively treated – as low as 4.
The chemical storage tanks need to be refilled occasionally.
- Acid injection
Acid injection is used for water with a high pH.
Water with a higher pH can have a soda-like taste that is eliminated with this treatment and the chlorination is improved.
Acid injection is a point-of-entry system.
Acid injection reduces pipe corrosion, since water with the pH above 9 corrodes brass, copper, zinc, aluminum and iron.
A solution of acetic acid is injected into water. Usually white vinegar is used, as it is the cheapest, but citric acid and alum are also an option, as well as more hazardous weak solutions of hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid if the pH is above 11.
The chemicals need to be refilled occasionally, while wearing the protective goggles, gloves and clothing.
- Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is used to reduce pH in alkaline water.
Carbon dioxide, CO2, is a colorless and odorless gas. It is a chemical compound composed of a carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms.
It is used as a pretreatment and sulfuric acid is added in the second step. The main purpose of this secondary acidification is to reduce the bicarbonate content and avoid calcium carbonate precipitation.
Carbon dioxide does not corrode the pipes and the equipment.
It was gives better control of pH than sulfuric acid. It shows self-buffering when reaching neutral pH levels. The self-buffering enables precise end-point control eliminating the danger of lowering the pH too much.
It can be utilized via a completely automated system.
Documents on TWN about pH and drinking water standards:
Media
Taxonomy
- Water
- Water Treatment Solutions
- Water Quality
- Water Quality Management
- water treatment
- Water Treatment & Control
- Water
- Water
1 Comment
-
nice pH refresher sheet. It is so basic, but I have seen some people get confused by pH.
1 Comment reply
-
Glad you like it!
-