Carbon Nanotubes Extract Groundwater Via the Roots of Tree Stumps
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Academic
In an article in Advanced Sustainable Systems, Professor Liangbing Hu and co-workers from the University of Maryland, USA, develop carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as a means to efficiently extract ground water via the roots of tree stumps by means of vaporizing the water under sunlight.
ByKieran O'Brien
The method and mechanism are exceptionally modest. Exposed tree stumps are simply coated with a layer of CNTs. Since CNTs are amongst the darkest materials known, they are capable of absorbing all light and converting this energy efficiently into heat, and since wood is an extremely poor heat conductor, when exposed to sunlight, the heat generated by the CNTs on the tree stump remains localized at the CNT/tree interface.
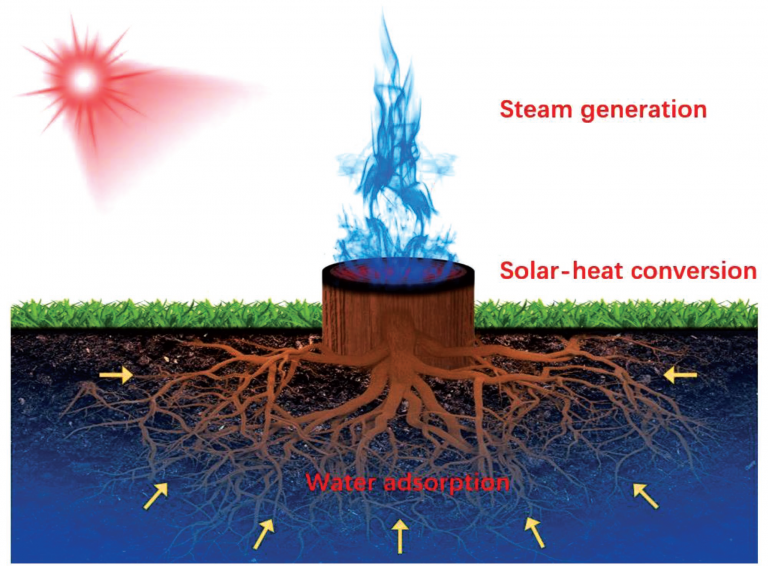
Image source: Advanced Science News
Therefore, when ground water is taken up naturally by the stump’s roots, and travels through the stump, this water is able to evaporate when it is heated up at the hot CNT surface. This process is highlighted in the figure below.
The efficiency of the CNT-coated tree stumps are remarkable. At just the thermal intensity of one sun, the evaporation rate of the ground water is one kilogram per meter-squared per hour, with a thermal efficiency of nearly 70%. However, by increasing this intensity to be the equivalent to that of 10 suns, the evaporation rates increases to 12 kilograms per meter-squared per hour, with a thermal efficiency of over 86%.
Such increase in solar intensity can be achieved by simply positioning a Frensel lens near the tree stump. In other words, no extra energy is required to increase the evaporation rate; just a sunny day and a large magnifying glass!
Read full article: Advanced Science News
The Paper: All Natural, High Efficient Groundwater Extraction via Solar Steam/Vapor Generation
https://doi.org/10.1002/adsu.201800055
Media
Taxonomy
- Resource Management
- Groundwater
- Water Resource Management
- Groundwater Assessment
- Groundwater Prospecting
- Groundwater Mapping
- Groundwater Quality & Quantity
- Groundwater Resource