Simple Arsenic Sensor Could Save Lives
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Technology
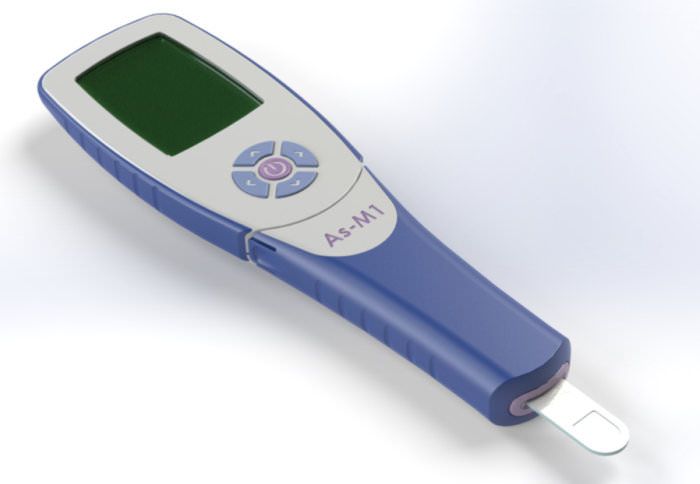
A low-cost, easy-to-use sensor which can test drinking water for arsenic in just one minute has been developed by Imperial and UCL researchers.
Worldwide, 140 million people drink water containing unsafe levels of arsenic, according to the World Health Organisation. Short-term exposure causes skin lesions, skin cancer and damage to the cognitive development of children, while long-term exposure leads to fatal internal cancers.
Source: Imperial College London
In one region of Bangladesh, one of the worst-affected countries, around 20% of all deaths are attributable to arsenic poisoning.
Researchers from Imperial College London and University College London (UCL) have developed a small, sensitive and accurate sensor, which produces an immediate measure of the arsenic level in water at a cost of less than $1 per test.
Currently available tests for arsenic need to either be carried out by scientists in a laboratory or using chemical test kits that produce toxic chemicals as by-products and take up to half an hour to give a result.
The new sensor, developed with BBSRC funding through the government’s Industrial Strategy, resembles the blood glucose meters used by diabetics. Once a drop of water hits the test strip, which is inserted into the sensor, it produces a digital reading of the arsenic level in one minute.
This would enable it to be used by local people in rural areas in low and middle-income countries, where the problem of arsenic poisoning is greatest and access to healthcare and technology is limited.
Creating the technology of tomorrow
Commenting on this game-changing product, Universities and Science Minister Sam Gyimah said: “This sensor to detect harmful levels of water contamination will make a huge difference across developing nations, potentially saving millions of lives.
“Too many people are exposed to dangerous levels of arsenic and this product is a clear demonstration of our Industrial Strategy in action, creating the technology of tomorrow and supporting the high-value, high skilled jobs that will make Britain fit for the future.”
The concept for the device was developed by Dr Joanne Santini from UCL and Professor Tony Cass from the Department of Chemistry at Imperial, whose earlier work led to the development of the first electronic blood glucose monitor.
Dr Santini had the idea of developing a sensor to detect arsenic in water when she discovered a microscopic organism that eats arsenic. She realised that an enzyme produced by this organism could be used to measure arsenic levels.
Bio Nano Consulting, a spin-out from Imperial and UCL, has patented the sensor design and, using a Smart Award from Innovate UK, created a prototype which it can produce in batches of up to 100.
Read full article: Imperial College London
Media
Taxonomy
- Drinking Water Security
- Treatment
- Treatment Methods
- Drinking Water Treatment
- Filtration
- Technology
- Filtration
- Drinking Water Managment
- Drinking Water
- water treatment
1 Comment
-
OKYD Ambassador UNDESA Focal Point Team on Global Goal 6 Clean Water & Sanitation welcomes & lauds low-cost, easy-to-use sensor which can test drinking water for arsenic in just one minute developed by Imperial and UCL researchers.