Hydrologic Modelling For Water Resources/Environmental Practitioners
Published on by Dr Harold Schroeter, Founder & CEO at Schroeter and Associates for Schroeter and Associates
Course Description - Winter/Spring2019
OBJECTIVES: Students who successfully complete this course will be able to:
- Describe the major computational elements in a representative selection of deterministic hydrologic models, including both continuous and event models, covering the range in space and time aggregation from annual-time-interval lumped models to highly distributed models of small watersheds with time intervals of one hour or less (e.g. one minute).
- Identify the physical quantities for which input data is required in the models described in (1) and give quantitative estimates of the range of values expected for each input quantity.
- Identify and describe computational procedure, using state-of-the-art algorithms, for various processes included in a hydrologic model. It may include
- Treatment of meteorological inputs (e.g. precipitation and air temperature).
- Computation of infiltration and superficial water generation
- Computation of watershed evapotranspiration.
- Calculation of soil water storage changes in space and time
- Computation of interception and depression storage.
- Calculate snow accumulation, ablation (melt) and re-distribution
- Calculation of contribution to ground water.
- Computation of overland flow, reservoir and channel (flood) routing.
- Make good initial estimates of key model input variables/parameters in the absence of calibration data.
- Describe the procedure used to calibrate a watershed model and the criteria used to test its success.
- Students will build a model of a sample watershed using representative hydrologic modelling software, and will learn how to calibrate and validate it, run sensitivity tests, and apply it for a practical application.
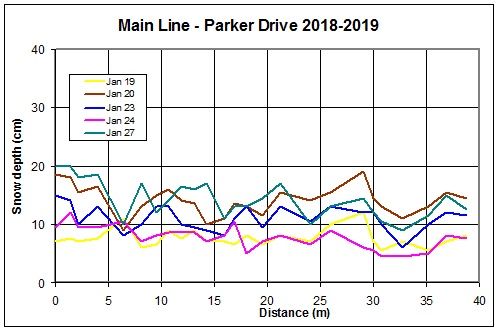
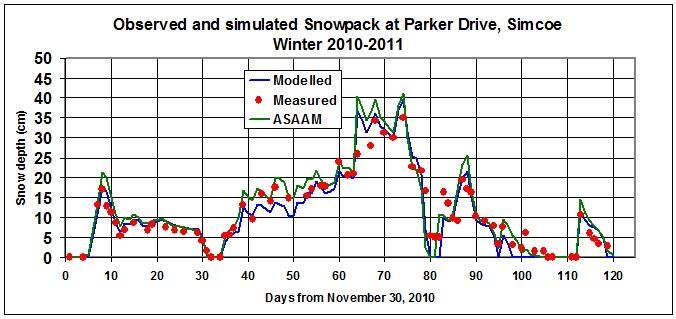
Media
Taxonomy
- Hydrological Modelling
- Sustainable Water Resource Management
- Hydrology
- Hydrologist
- Flood prediction
- Hydrological Modelling
- Water Resources Management
- Hydrological modelling of climate change