How does GIS for Water Leak Detection Work?
Published on by Vishakha Rajput, Previous COO The Water Network at AquaSPE AG in Technology
Water leaks cost water utilities and consumers a lot of money. The sooner the leakage is detected, the less clean water will go to waste.
 Water loss is something that can be prevented if the leakage is detected in time and if it is rapidly fixed.
Water loss is something that can be prevented if the leakage is detected in time and if it is rapidly fixed.
The problem with detection is that only bigger leaks get detected, often even they get noticed and reported after the pipe bursts.
Satellites can detect leaks as small as 0.5 l/min.
As well as being the most precise, they are the fastest. They do not require any manual labor nor anyone on the field. Everything
Satellites use microwaves echography.
Microwaves are electromagnetic radiation with the wavelengths between 1 m and 1 mm and frequencies between 300 MHz (100 cm) and 300 GHz (0.1 cm).
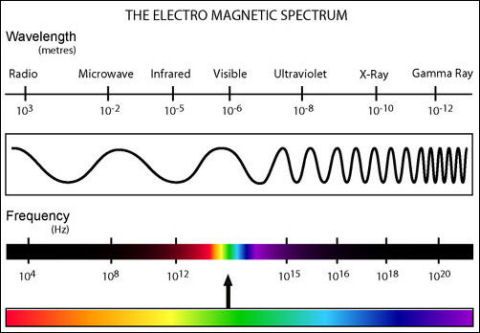
Image: Electromagnetic wavelengths
Image source: keywordsuggest.org/gallery/1068780.html
Specifically, microwaves are chosen because they do not diffract on rough terrain (hills), they do to reflect from the ionosphere and, most importantly, they differentiate clean treated water from other kinds (dirty water, saltwater, etc.).
Microwaves are absorbed by water and metal and do not reflect from it so it is easy to detect a leak.
Moreover, the dielectric constant (relative permittivity) of pure water makes it easy to detect a leak.
With the increase of the dielectric constant, the electric flux density will increase. (Remember that microwaves are electromagnetic waves!)
Water has a high dielectric permittivity, which enables the detection and measurement of water in soil.
The exact wavelength of microwaves from the satellites is, therefore, set based on the very specific dielectric constant of pure water, in addition to the ability of the microwave with a specific wavelength to penetrate the ground.
Moreover, the frequency has effect and needs to be considered since the microwaves on different frequencies are differently absorbed by vapour in the atmosphere.
The images collected by satellites are overlaid on GIS systems and processed. This shows a clear image of water leaks and the position of pipelines in the infrastructure.
Sources:
As far as I know, Utilis is currently the only company who uses this technology.
Read TWN's interview with Lauren Guy, CTO and co-founder of Utilis.
Media
Taxonomy
- GIS & Remote Sensing Technology
- GIS
- Leakage Detection
- GIS for network
- Leakage
- GIS & Remote Sensing
1 Comment
-
Other companies working on satellite leak detection include http://www.rezatec.com/ and IMG - Intelligent Modelling Geospatial (https://www.linkedin.com/company-beta/10665222/), both in the UK