More Trees Help Water Sanitation, Reduce Child Deaths
Published on by Water Network Research, Official research team of The Water Network in Academic
A University of Vermont-led study of 300,000 children in 35 nations says kids whose watersheds have greater tree cover are less likely to experience diarrheal disease, the second leading cause of death for children under the age of five.
Published in Nature Communications, the study is the first to quantify the connection between watershed quality and individual health outcomes of children at the global scale.
“Looking at all of these diverse households in all these different countries, we find the healthier your watershed upstream, the less likely your kids are to get this potentially fatal disease,” says Taylor Ricketts of UVM’s Gund Institute for Environment.
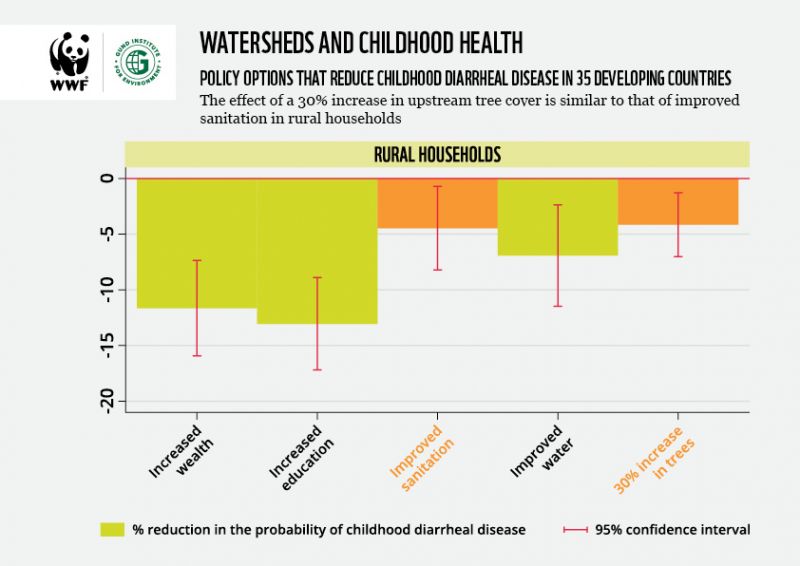
Surprisingly, the team predicts that a 30 per cent increase in upstream tree cover in rural watersheds would have a comparable effect to improved water sanitation, such as the addition of indoor plumbing or toilets.
“This suggests that protecting watersheds, in the right circumstances, can double as a public health investment,” says Brendan Fisher of UVM’s Gund Institute and Rubenstein School of Environment and Natural Resources. “This shows, very clearly, how ‘natural infrastructure’ can directly support human health and welfare.”
The research is the first to use a massive new database that will enable “big data” approaches to study links between human health and the environment, globally. The database features 30 years of USAID demographic and health surveys, with 150 variables for 500,000 households, including spatial data on the environment.
“We are not saying trees are more important than toilets and indoor plumbing,” says Diego Herrera, who led the paper as a UVM postdoctoral researcher, and is now at Environmental Defense Fund. “But these findings clearly show that forests and other natural systems can complement traditional water sanitation systems, and help compensate for a lack of infrastructure.”
The researchers hope the findings help governments and development agencies to improve the health and environment of children around the world. They add that more research is needed to more fully understand exactly how watershed forests impact the risk of diseases like diarrhea, which has many causes, including waterborne pathogens.
The research covers 35 nations across Africa, Southeast Asia, South America and the Caribbean, including Bangladesh, Indonesia, Philippines, Nigeria, Colombia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.
The study was supported by the National Socio-Environmental Synthesis Center (SESYNC), Luc Hoffmann Institute and WWF, along with The Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation and The Rockefeller Foundation as part of the Health & Ecosystems: Analysis of Linkages(HEAL) program (now Planetary Health Alliance).
Source: The University of Vermont
Read full study: Nature Communications
Media
Taxonomy
- Public Health
- Diarrhea
- Watershed Management
- Ecosystem Management
- Sanitation
- Ecosystem Management
- Watershed
- Integrated Watershed Management
- Water & Sanitation
- Sanitation & Hygiene
- Sanitation & Hygiene
- Control of Diarrhoeal Diseases
- Water Sanitation & Hygiene (WASH)