How is electrolysis technology is helpful in reducing the TDS?
Published on by Mekhela Anneliese in Technology
Can someone tell me how the electrolysis technology is helpful in reducing the TDS?
Can it also be helpful in removing hardness of water?
Our water is also detected with sulfur content - what should we do?
Taxonomy
- Water
- Potable
- Drinking Water Security
- Electrolosis
- COD Removal
- Drinking Water Treatment
- Water Treatment Solutions
- Drinking Water Managment
- Drinking Water
20 Answers
-
The Water Network research team has consolidated an answer to the above question.
Further input from members is welcome and appreciated.
Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) are all the minerals, salts, metals and ions (cations and anions) in the water.
Pure water is a universal solvent – it easily dissolves the inorganic salts (Ca, Mg, Na, bicarbonates, chlorides and sulphates) and some of the organic matter, hence the dissolved solids in water.TDS in water has different origins - natural sources (leaves, silt, plankton), sewage, urban run-off, industrial wastewater, and chemicals used in the water treatment process.
They also come from rocks and air that contain certain minerals.
Another source of TDS are the metals water picks up while going through pipes while being distributed.TDS is directly related to the purity of water and the quality of water purification systems and affects everything that consumes, lives in, or uses water.
TDS concentration is a secondary drinking water standard.
Therefore, elevated levels are not a health hazard, but the water has greater hardness, may create deposits and be corrosive, water may be coloured and have a salty and brackish taste.
By the EPA standards TDS should not exceed 500 mg/l.
By the WHO standards TDS in water classify as following:
Level of TDS [mg/l]
Rating
Less than 300
Excellent
300 - 600
Good
600 - 900
Fair
900 - 1,200
Poor
Above 1,200
Unacceptable
For comparison, it is useful to state that most aquatic ecosystems with different fish fauna tolerate TDS levels of 1000 mg/l.
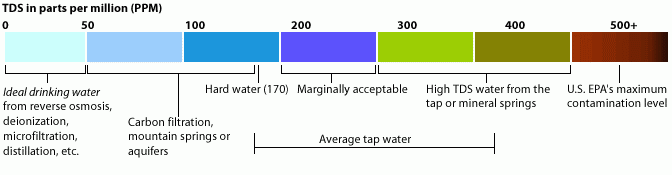
Diagram 1: TDS in ppm
Source: tdsmeter.com/what-is#whatTreating TDS depends on which solids are dissolved in the water:
- If TSD are calcium, magnesium or iron a water softener should be used.
- If concentrations of sodium, chloride, or potassium are elevated reverse osmosis should be used as a water treatment.
- For high to iron, manganese, arsenic concentrations or total hardness in general, other methods should be used.
* TWN Team has written a detailed answer on how to remove As from drinking water. Find it here.
* Read about total dissolved solids removal here.
Electrolysis
Electrolysis is a technique which uses direct electric current to initialize a reaction that wouldn’t otherwise occur on its own.
The electric current passes through a ionic substance (conducts electricity) which is molten or dissolved in a solvent.The voltage needed for the reaction to occur is the decomposition potential.
When the electrodes are put in the ionic substance and the charge is released, the decomposition potential is passed through the ions which are attracted to the electrode of the opposite charge. On the anodes, the ions are made into molecules and atoms.
Electrolysis decomposes the Total Dissolved Solids (TDS) into cationic (positive ions) and anionic (negative) from as the current flows through the cathode (negative) and anode (positive). Cations are attracted by the cathode and anions by the anode.
Reactions occur on the electrodes - reduction on the cathode and oxidation on the anode.
Reduction is a chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of the atom is changed - electrons are gained and the oxidation state is decreased.
Oxidation is a chemical reaction which involves the electron transfer process as the electron is stripped, lost and the oxidation state is increased.
If more than one reaction is possible, the reaction which needs the least energy will occur.
How the electrolysis is used to treat TDS depend on the type of TDS.
Electrolysis is not used to treat water hardness.
However, the document “Water Hardness Removal for Industrial Use: Application of the Electrolysis Process” may be useful to read. It says about the production of primary coagulant during electrolysis improved flotation of both calcite: calcium carbonate, CaCO3, and magnesium hydroxide, Mg(OH)2.Sulfur water
Sulfur water is caused by hydrogen sulfide which gives water the rotten-egg odor.
- Most people can smell hydrogen sulfide in water with a concentration of as little as 0.5 parts per million (ppm).
- Waters with concentrations from 0.5 to 1 ppm smell “musty” or “swampy.”
- Concentrations greater than 1 ppm smell like “rotten eggs” and are corrosive to plumbing.
To deal with sulfur water, it is useful to first establish why it is there in the first place:
1. Odor only in hot water:
If the stench occurs only in hot water the source is probably a reaction between an anode rod in the water heater and naturally occurring sulfate ions in the water.
The anode rod is made from magnesium or aluminium and the Mg one is more likely to cause the odor so replacing it with the aluminium rod is the first step to the solution. If the odor still occurs, there are two possible solutions – removing the anode rode completely or removing the sulfate ions.
Since the anode rod is protects the water heater tank from corrosion, removing the rod could shorten its life. However, corrosion inhibitors can prevent this.
Sulfate can be removed with a dealkalizer (removes alkalinity ions from water).
2. Odor in the cold water which goes away after water flows:
The source is most probably sulfare-reducing bacteria (SRB). They are not pathogenic but they cause an unpleasant odor by “breathing in” sulfate ions and “breathing out” hydrogen sulfide.
If there is no flow, the odor will occur and decrease as the water flows.
SRB are treated with shock chlorination of the entire system (chlorine stays in the system for several hours) but if this doesn’t eliminate the odor, continuous chlorination may be necessary.
3. Odor in both hot and cold water which doesn’t decrease with the flow:
This is caused by hydrogen sulfide from the aquifer source. Hydrogen sulfide is a gas formed by the decay of organic matter.
The treatment depends on the level of hydrogen sulfide and other contaminants, but also the flow rate and daily water usage.
Hydrogen sulfide is not a regulated drinking water standard since it is considered a nuisance and has no health risks for humans.Water with such high concentrations that would pose a risk is not palatable.
0.5 mg/l gives water a taste and rotten egg smell.Treatment usually relies on the oxidation of hydrogen sulfide gas into elemental sulfur.
- If hydrogen sulfide concentrations are above 6 mg/l chlorination is recommended.
- If hydrogen sulfide concentrations do not exceed 6 mg/l and water pH is above 6.8 an oxidizing filter, such as manganese greensand, is recommended.
Chlorination
Continuous chlorination is a common method for hydrogen sulfide treatment.
Chlorine kills the bacteria so it is a typical water treatment method.
Chlorine is usually administered as sodium hypochlorite and reacts with sulfide, hydrogen sulfide, and bisulfide forming compounds which do not cause bad taste or odor in water.
It is recommended to add 2 mg/l of chlorine for every 1 mg/l od hydrogen sulfide.
Chlorine is supposed to be added before the mixing tank and the water should have 20 minutes to get in contact with it in a sufficient storage space.
After this treatment, the water should pass through a depth filter or an activated carbon filter, to remove the remaining sulfur or excess chlorine.
Chlorination systems come in pellet-drops or liquid-chemical feed.
Chlorination systems may be costly are the constant chemicals addition is required and the system needs to be maintained regularly.
Manganese greensand
Manganese greensand is used as a hydrogen sulfide treatment method if its concentration is less than 5 mg/l.
Hydrogen sulfide gas is oxidized to solid sulfur particles, which get filtered, by special coating on a manganese greensand filter. Prechlorination is recommended.
The greensand should periodically be regenerated or recoated with potassium permanganate.
Manganese greensand comes in a natural and synthetic form. They have the same efficiency but the synthetic requires less backwash water and softens the water .
Aeration
Aeration is physical removal of hydrogen sulfide by agitating the water and stripping the hydrogen sulfide in a container.
Its greatest effect is achieved when hydrogen sulfide concentrations do not exceed 2 mg/l.
Air is introduced into water with an air compressor or blower.
Ventilation is required.
Aeration doesn’t require any chemicals and is not too expensive.
If hydrogen sulfide is oxidized to sulfide, bisulfide or solid sulfur particles which need to be filtered.
Ozone
Ozone oxidizes sulfides to solid sulfur and breaks down the slime produced by sulfur bacteria.
Ozone can treat high sulfide levels efficiently.
To remove hydrogen sulfide as a gas, ventilation is required.
Prefiltration is recommended and postfiltration is maybe necessary for the removal of oxidized solids.
Catalytic carbon
Catalytic carbon is activated carbon with a modified carbon surface.
Activated carbon is only effective in removing low concentrations of hydrogen sulfide and needs to be replaced once the filter is saturated.
Catalytic carbon has the ability to promote or catalyze chemical reactions, along with adsorption.
Catalytic carbon adsorbs sulfides and, with the presence of dissolved oxygen (minimum 0.4 mg/l), oxidizes them and converts to no objectionable compounds.
It doesn’t require any chemicals.
Ion exchange
Ion exchange is a physical- chemical process in which ions are swapped between a solution phase and solid resin phase. The process is named due to some ions being trapped and others released.
There are two types of ion exchange: cation exchange water softeners and anion exchange units.
For hydrogen sulfide, the anion exchange resin column is recharged with sodium chloride, and then chloride replaces sulfide.
Low water flow is a disadvantage along with elevated chloride levels. Moreover, anion exchange lowers the water pH making it corrosive.
Related questions:
- What is the best range for TDS in potable water?
- How to reduce TDS level in golf course irrigation water?
Additional resources:
WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality
EPA drinking water standards and health advisories table
Hydrogen Sulfide in Household Drinking Water
Your Household Water Quality: Hydrogen Sulfide And Sulfate
Water Hardness Removal for Industrial Use: Application of the Electrolysis Process
Read more related content on total dissolved solids (TDS) here.
-
I have more than 20 years experience in this field. Precipitation of lime-scale through the use of zinc ions is well proven. www.ecobrook.co.uk or contact me for the latest technology news and advances in the electrolysis by zinc anode method. We have made some exciting advances and I will be presenting a significant improvement in performance for this type of technology in the Spring of 2014.
1 Comment
-
sir is there any advanced simple technique for removal of TDS in water apart from RO and common ion exchange techniques
-
-
Electrolysis Technology
Hi Mekhela,
Electrolysis Technology is helpful in reducing TDS by decomposing the Total dissolved solids in to Cationic and Anionic form with the application of Anionic & Cathodic sources or external current source. Like take example of Electrodeionisation units which we are calling as EDI are using the same method to decompose and separate TDS with the help of Anion Exchange Membrane and Cation Exchange Membrane. But this technology has limitations in terms of feed water characteristics. As far as EDI is concerned it cannot remove hardness. If water contains Sulphur Content try putting RO System or De Mineraliser with suitable pre-treatment in place.
Regards,
Ambarish
-
Thanks everyone for your replies. I am looking into all your suggestion carefully and will adopt the best suited solution for our project site. I will keep you posted with updates.
-
technology to reduce TDS
three proven technology to reduce TDS
Reverse Osmosis (RO) remove TDS by forcing the water, under pressure, through a synthetic membrane. The membrane contains microscopic pores which will allow only molecules smaller than 0.0001 micron to pass through. Since the molecules of dissolved metals and salts are large compared to the water molecules, the water will squeeze through the membrane leaving the metals and salts behind.
A professional Reverse Osmosis system is capable of removing 90-99% of the dissolved mineral salts from water. A pre-filter is usually required to protect the membrane and remove organics.
The Pureoflow is a type of whole business or whole house reverse osmosis that is used as both a salt-free water softener, and a purifier. Whole house systems like the Pureoflow have the added benefit of protecting water heaters from corrosion, in addition to high quality drinking water.
Distillers are better known as “stills.” Stills work by heating small amounts (less than 2 gallons) of water to produce steam. The steam is then collected and condensed back into water. The dissolved mineral salts will not vaporize and are left behind in the heating chamber.
Stills require frequent, rigorous cleaning to remove the baked-on mineral salts. They also produce a “flat” taste and acidic water which has kept them from becoming a popular drinking water solution.
Deionization (DI) Systems pass water through a resin cartridge that attracts the dissolved solids, producing a high-purity water. Because DI cartridges have a limited life and require frequent replacement they are generally not used for high volume applications.
YOU CAN VIEW THE WEBSITE OF ASPEN FLUID LOGISTICS.
-
Hi Mekhela: Electro Dialysis may be one of the best Electrolysis Technology. You can apply this to even nery high TDS Contaminants more than 150,000TDS. But the weak point of this technology is high power consumption.
-
TDS reduction
Yes its helpful like if there are cations free in solution as Na+ similar may be reduced ultimately TDS will decrease, does it helps or more explanation is needed?
-
Plasma Activated Water (PAW) Technology solves many problems simultaneously. While the technology is not yet available commercially, we are working on that and will communicate further once that process is underway. In the meantime, the scientists involved gave me permission to report on observations when humans drink this water here: http://kindrop.abc4all.net To learn more about their research and validation/independent laboratory findings watch this PPT: Water for the World: http://kindrop.abc4all.net/files/200101_200200/200157/well-water4world.ppt
-
Hi Mekhela I agree with Abolfazl and I would add that sulphur is another problem which you have to deal with. Your question is very wide. Please be more specific.
-
Electrical pulses not electrolysis can clump solids together to aid in filtration. There are other versions for salt free water softening. Is the sulphur a gas or dissolved or part of the TDS ? Gas can be removed by using a tank Activated charcoal Filters are available to remove dissolved sulphur rust and other minerals. Ozone or infrared can kill bacteria
-
TDS
Hello Anneliese,
see: www.baleari.de
EFFECTS OF THE LEKRA WATER ACTIVATOR
Coffee, tea and food have a more intense taste.
Reduction of lime residue in pipelines.
Easy removal of lime residue on tiles, fixtures, etc.
Longer operating period for technical equipment such as dishwashers, washers etc.
After years of research, development and applications, all effects ascertained to be connected with the use of a LEKRA Water Activator have been positive.
-
First you should to give some more information: - water for? - Quantity? - Quality? - Already applied technology? etc. etc. Kind regards, Miroslav
-
Hello Mekhela, You can use Capacitive De-ionization to reduce TDS, Hardness and other contaminants from water. We are building treatment plants using this system and it has shown good results as Point of Entry based treatment. CDI is in a way uses the principle of Electrolysis. Hope this answers your question.
-
How electrolysis can help reducing TDS!
Dear Anneliese, Total Dissolved Solids (often abbreviated TDS) is a measure of all inorganic and organic substances contained in water in molecular, ionized or micro-granular (colloidal sol) suspended form. The operational definition is solids that are small enough to pass a two-micrometer filter. Part of these dissolved solids are salts and metals allowing water to have a slight conductive behaviour. If such water get in contact with metals a natural electro-chemical process called electrolysis will occur. This process can dissolve or remove parts of the solids from the water. Corroding ductile iron pipes for example introduce iron ions in the water. When water is heated, this electrical process can be accelerated which is for example a problem for water heaters.
The natural electrolysis can be reversed and accelerated by forcing an opposite current with a sacrificial anode. This controlled electrolysis can reduce certain solids in the water reducing the overall TDS but there is more to it than just running a current and having an sacrificial anode to ensure the desired effect. You need the right chemical reaction adapted to your water and environment.
Good luck
K.
-
Electrolysis
Electrolysis involves sending a current through a solution to drive a chemical reaction. It is how Chlor-Alkali plants produce Chlorine and Caustic from sea water or brine. The pH is lowered at the anode where oxidation occurs in the solution and the pH is raised at the cathode where reduction occurs in the solution.
Often hydrogen gas will evolve at the cathode.
How exactly it effects TDS will depend entirely upon the composition of the TDS. If the current is not strong enough or the voltage is wrong, it is very possible that it will do little or nothing.
I am aware of a device called The Green Machine that uses the higher pH at the cathode to precipitate calcium carbonate. This is then removed in some method that I am not familiar with to lower the over all hardness of the solution and thus soften the water to some degree.
I am not aware of an electrolytic method of sulfur removal, though H2S is a water soluble gas. Aeration has been effective for sulfur removal and acidification would be expected to improve that. Perhaps there is a device that aerates at the anode to remove sulfur. I am just not aware of it.
One thing you should be very cautious about is people trying to sell you a device that removes nothing from the water but somehow solves your problem by changing something in the water that no one, not even they, can detect. If it removes nothing from the water and the chemical changes cannot be detected, most likely nothing happened and all it will do is remove some money from you.
-
Hi Anneliese, you can use electrolysis to reduce hardness of water. Also is possible to disinfect it. Send me your detailed question if you like more information. Regards
-
Use of electrolysis technology
Hi my friend,
you can ues this technology for less than 2000 tds (brackish water) for desalination
if you want more information please send me your detail question
have good time.
-
Removing TDS from water
Reverse Osmosis remove TDS by forcing the water, under pressure, through a synthetic membrane. The membrane contains microscopic pores which will allow only molecules smaller than 0.0001 micron to pass through. Since the molecules of dissolved metals and salts are large compared to the water molecules, the water will squeeze through the membrane leaving the metals and salts behind.
A professional Reverse Osmosis system is capable of removing 90-99% of the dissolved mineral salts from water. A pre-filter is usually required to protect the membrane and remove organics
-
electrolisis reducing TDS
pls refer
http://nopr.niscair.res.in/bitstream/123456789/8603/1/IJCT%2012%282%29%20164-169.pdf
-
Electrolysis by a sacrificial anode will NOT change water qualities. the hardness will stay but it is no longer aggressive. Scale is percipitated through the zinc ions and will NOT percipitate again. so we solve the problem without softening water, which can make water aggressive and corrosive again. www.aquabion.com